Reviving Agri-Research
Syllabus Areas:
GS II - Economy (Agriculture and Food Security)
Origin of the term “Green Revolution”: Coined by William S. Gaud, Administrator of USAID, in a 1968 speech.
- The revolution aimed to combat hunger via high-yielding varieties of crops, better irrigation, and fertilizers.
- It succeeded mainly in India and not in most developing countries due to strong institutions like ICAR and scientists like S. Swaminathan.
Key Indian Institutions Behind the Green Revolution
- ICAR (Indian Council of Agricultural Research)
- IARI (Indian Agricultural Research Institute)
- PAU (Punjab Agricultural University)
- CIMMYT (Mexico-based, collaborated on wheat research)
Importance of International Collaboration
- India benefited from international collaboration, especially USAID and Rockefeller Foundation.
- CIMMYT (Mexico) provided germplasm and breeder seeds for wheat development.
- Philanthropic and aid-based models like Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR), International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) supported India’s agri-research ecosystem.
What is Germplasm?
Germplasm = the raw genetic material of plants used in breeding better crops.
It includes: Seeds, DNA, Pollen, Tissues (from roots, shoots, etc.)
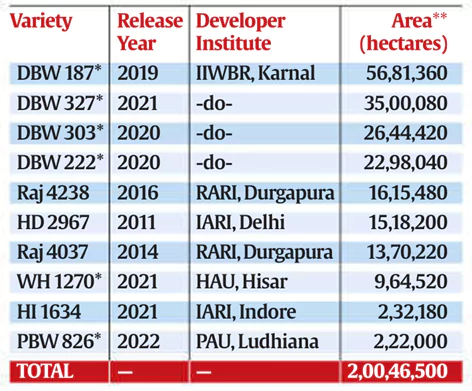
Top 10 Wheat Varieties in India (Cultivated Area-wise):
What is USAID?
USAID stands for the United States Agency for International Development.
- Founded: 1961 (by an executive order of President John F. Kennedy)
- Headquarters: Washington, D.C., USA
- Type: Independent agency of the U.S. federal government
- Motto:"From the American People"
USAID’s Role in the Green Revolution (India-specific):
- USAID funded agricultural research programs in India.
- Collaborated with Indian institutions like ICAR and IARI.
- Supported the import of high-yield wheat varieties from Mexico’s CIMMYT, facilitating India’s wheat revolution in the 1960s.
- Brought in technical expertise and scientific exchange, helping India solve its food security crisis post-Independence.
Recent Challenges
- US support via USAID has slowed.
- Funding and institutional support for ICAR institutes, especially wheat-breeding centers, are now uncertain.
- Scientists and institutions seek more autonomy and funding control domestically.
The Argument for More Indian Ownership
- India now has strong internal capacity, including experienced scientists and world-class institutions.
- Government is urged to increase funding and global leadership in agri-research.
- Concerns: India shouldn’t just be a testing ground; it must also influence global agricultural research priorities.
Future Needs
- Climate-resilient and high-yield varieties are needed to adapt to changing monsoon and temperature patterns.
- Indian institutes are releasing new varieties (e.g., HD 3410, HD 3717, HD 3755, WB 373).
- Continued R&D is essential for food security and export potential.
Prelims Questions:
- Which of the following correctly explains the role of USAID in India’s Green
Revolution?
- USAID provided subsidies for fertilizers and irrigation to Indian farmers.
- USAID directly implemented land reforms in India during the 1960s.
- USAID funded the import of high-yield wheat varieties and collaborated with Indian research institutions.
- USAID partnered with NABARD to provide rural credit.
- Consider the following statements about germplasm:
- Germplasm includes only the seeds of plants used for breeding.
- It is used for developing disease-resistant and high-yielding crop varieties.
- Germplasm conservation is vital for preserving agricultural biodiversity.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- Match the following international institutions with their primary focus:
- CGIAR 1. Policy research on agriculture and food systems
- IRRI 2. Global partnership of agricultural research centers
- IFPRI 3. Rice-specific research and seed development
Options:
- A-2, B-3, C-1
- A-1, B-2, C-3
- A-3, B-1, C-2
- A-2, B-1, C-3
- CGIAR: umbrella body for international agri-research centers.
- IRRI: focused on rice.
- IFPRI: food policy research.
Answer: c) USAID funded the import of high-yield wheat varieties and collaborated with Indian research institutions.
Explanation: USAID (United States Agency for International Development) was instrumental in supporting India’s Green Revolution by facilitating research partnerships and funding seed imports from CIMMYT.
Answer: b) 2 and 3 only
Explanation: Germplasm includes all forms of genetic material—seeds, tissues, even DNA—and is crucial for crop improvement and biodiversity.
Answer: a) A-2, B-3, C-1
Explanation:
Mains Question:
- What is the role of agricultural R&D in mitigating the impact of climate change on food production? 150 Words 10 Marks















