Fight Against Cancer
Cancer treatment remains financially burdensome, with 1.6 million new cases and 800,000 deaths in India in 2023, rising further.
History of Cancer Research and Treatment in India
- The earliest cancer cases in India were documented in the 17th century .
- Between 1860-1910 , Indian medical practitioners conducted audits and published cancer case series.
- 1917-1932: Nath and Grewal’s study confirmed cancer as a major cause of death among middle-aged and elderly Indians.
- 1941: Tata Memorial Hospital was established by the Sir Dorabji Tata Trust, later evolving into Tata Memorial Centre (TMC) in 1966 .
- 1920s: Adoption of radiotherapy (radium brachytherapy) for cancer treatment in India.
- 1937: The National Cancer Institute Act (USA) influenced India's cancer research and treatment policies.
Notable Indian Scientists in Cancer Research
- Dr. Vasant Ramji Khanolkar: "Father of Pathology in India"; worked on cancer epidemiology.
- Dr. Kamal Ranadive: Studied the link between cancer and viruses; established India’s first tissue culture research lab.
- Dr. Indraneel Mittra: Led a breast and cervical cancer screening trial for 150,000 women .
- Dr. Siddhartha Mukherjee: Wrote "The Emperor of All Maladies" , a Pulitzer Prize-winning book on cancer.
- Dr. Nina Bhardwaj: Leading research in cancer immunotherapy .
- Dr. Ashok Venkitaraman: Studied how BRCA2 gene mutations cause cancer.
- Dr. Kumaravel Somasundaram: Focused on glioblastoma research .
- Dr. Anil Suri: Discovered SPAG9 , a tumor antigen used for cancer immunotherapy.
What are T cells
- T cells are a type of white blood cell in the immune system that help fight infections and cancer. They recognize and destroy infected or abnormal cells, playing a crucial role in immunity.
What is CAR-T cell Therapy?
- CAR-T cell therapy (Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-cell therapy) is an advanced form of immunotherapy that modifies a patient’s own T cells to recognize and attack cancer cells. It is a personalized treatment used primarily for blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma.
This therapy follows a multi-step process
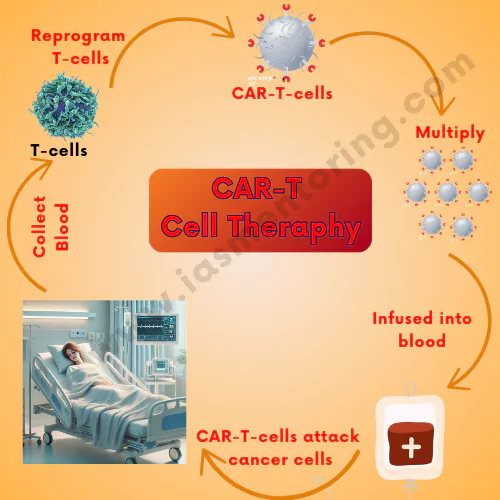
The important step in the therapy is
- In a specialized lab, scientists genetically modify the extracted T cells by inserting a gene that encodes a Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) .
- This receptor helps T cells recognize and attack specific cancer cells .
- The modified CAR-T cells are grown in large numbers in a laboratory.
- Once enough CAR-T cells are produced, they are prepared for infusion back into the patient.
Many people believe that a cancer diagnosis equates to an inevitable fatal outcome. However, advancements in medical research, early detection, and improved treatments have significantly increased survival rates for various cancers.
India’s Advancements in Cancer Treatment
- NexCAR19 (2023): India’s first indigenous CAR T-cell therapy , developed with US collaboration.
- Halcyon Radiotherapy System: Improved precision in cancer treatment.
- Government investment under the National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Disease, and Stroke to enhance healthcare infrastructure.
Government Initiatives for Cancer Control
- National Cancer Control Programme (1975): Aimed at early cancer detection and treatment.
- NPCDCS Scheme: Strengthens oncology facilities in medical colleges and district hospitals.
- Ayushman Bharat Scheme: Offers financial aid for cancer treatment.












