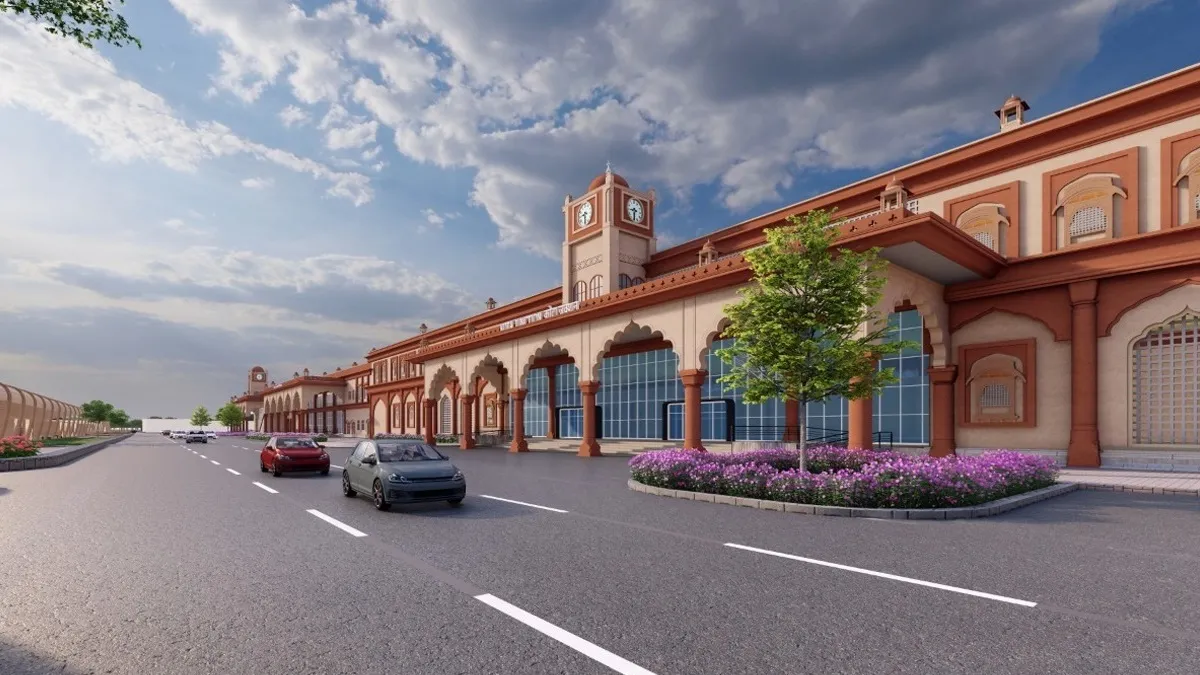
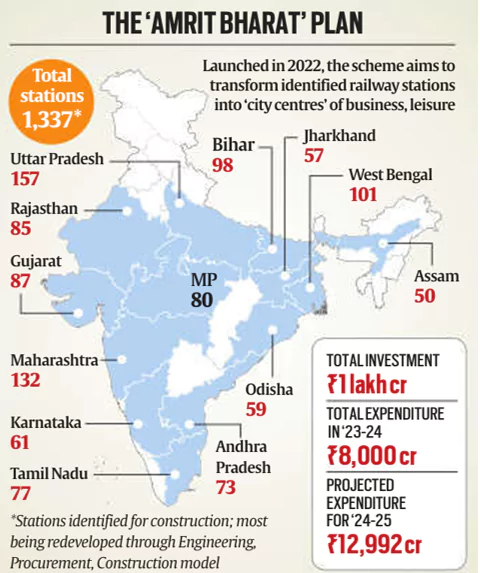
Amrit Bharat Station Scheme
- The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme was launched on August 6, 2023, by the Ministry of
Railways.
-
Aim: To redevelop 1,337 railway stations
across the country into
world-class city
centres .
-
Objective:
-
Transform railway stations with airport-like facilities .
-
Integrate local culture and heritage in station
architecture.
-
Enhance passenger amenities like executive lounges, food
plazas, free
Wi-Fi, and modern retail spaces.
-
Estimated Total Cost: ₹1 lakh crore.
-
Budget Allocation:
-
FY 2023-24: ₹8,000 crore spent.
-
FY 2024-25: ₹12,993 crore allocated.
Facilities Proposed Under the Scheme
-
Airport-like amenities: Executive lounges, business centres, and
modern retail
shops.
-
Free Wi-Fi services, air-conditioned waiting halls, and modern escalators.
- Integration of Local Culture: Each railway station will reflect
local art,
culture, and heritage .
-
Example: Ayodhya Dham Railway Station built with a
temple-like façade,
depictions from the Ramayana, and mythological motifs.
-
Sustainability & Smart Infrastructure: Improved traffic flow,
pedestrian pathways,
parking facilities, and multi-modal transport hubs.
-
Incorporation of eco-friendly construction practices.
Major Stations Under Development
- Jammu Tawi, Gorakhpur, Lucknow Charbagh, Prayagraj Junction, Sabarmati,
Surat,
Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus (CST), Muzaffarpur Junction, etc .
- A total of 80 priority stations are being continuously monitored
by the Railway
Ministry.
Two Implementation Models of the Project:
- EPC Model (Engineering, Procurement, and Construction):
-
The contractor handles the entire project from design to execution
.
-
Used for most projects to avoid delays.
-
Benefits of EPC Model:
-
Avoids cost overruns and project delays.
-
Ensures faster completion of projects.
-
PPP Model (Public-Private Partnership):
-
Used in major commercial hubs like Pune, Delhi Junction,
Vijayawada, and
Chennai Central .
-
Private sector involvement ensures faster completion and modern
facilities.
-
Benefits of PPP Model:
-
Involves private funding, reducing the financial burden on the
government.
-
Encourages private companies to develop infrastructure and operate
commercial facilities.
Economic and Social Impact
-
Economic Multiplier Effect:
-
Boost to the local economy due to increased commercial
activities around
railway stations.
-
Enhanced revenue through commercial outlets like malls, food courts, and
lounges.
-
Increase in tourism and local business growth.
-
Employment Generation:
-
Direct and indirect employment generation in construction, operations,
retail, and tourism sectors.
-
Around 20,000 railway engineers trained across 68 railway
divisions
to
execute the project.
-
Improved Passenger Experience:
-
World-class facilities for passengers like lounges, escalators, AC waiting
rooms, and multi-modal transport hubs.
-
Clean and hygienic premises with modernized washrooms and better
accessibility for disabled persons.
Funding and Budget Allocation
-
Budget Allocation:
-
FY 2023-24: ₹8,000 crore spent.
-
FY 2024-25: ₹12,993 crore allocated
- No Shortage of Funds:
-
The Railway Minister confirmed that funds are continuously being allocated
based on project progress.
-
Customer Amenities Fund:
-
The funds for the project have been categorized under "Customer
Amenities"
in the Railway Budget.
Challenges Addressed Under the Scheme
-
Previous Failures:
-
Earlier station development projects failed due to poor planning and
contractor inefficiency.
-
Lack of integration between infrastructure and commercial development.
-
Current Strategy:
-
The Railway Board conducted stakeholder workshops across
68 railway
divisions.
-
Around 20,000 railway engineers were trained for smooth
project
execution.
-
Model tender documents were prepared to avoid project delays.
Role of Local Culture and Heritage
-
The project aims to promote local art and culture in station
designs.
-
Example:
-
Ayodhya Dham Railway Station:
-
Temple-like architecture, mythological motifs, and Ramayana
murals.
-
Gandhinagar Station:
-
Integration of Gujarati art and heritage.
-
This approach aligns with the Vocal for Local and
Cultural
Revival
initiatives.
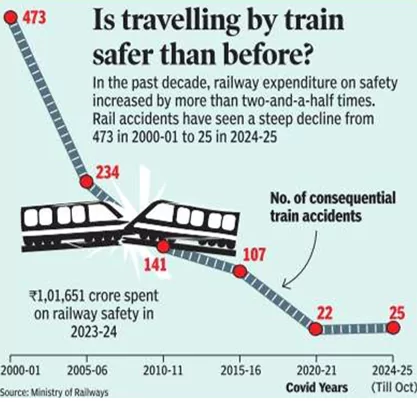
Is travelling by ‘Train’ safer than before?