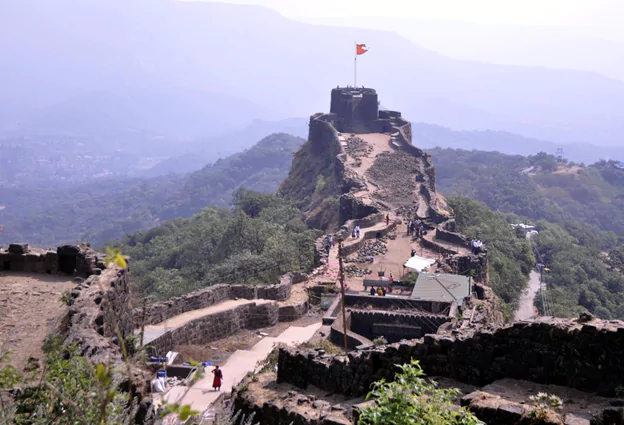
Maratha Military Landscapes - UNESCO WHS
Syllabus Areas:
GS I - Art & Culture
General Essay - Cultural diplomacy, heritage preservation
On July 5, 2025, at the 47th session of the UNESCO World Heritage Committee (WHC) held in Paris, the Maratha Military Landscapes of India was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage List, making it India's 44th World Heritage site.
What are the Maratha Military Landscapes?
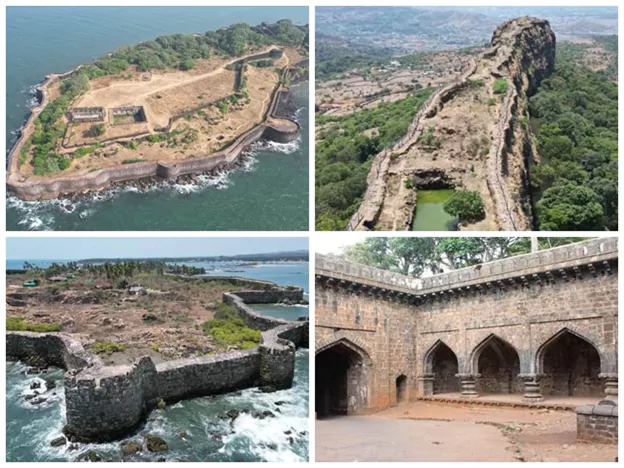
- A network of 12 forts across Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu, ranging from coastal outposts to hill forts.
- Represents the military vision, architectural ingenuity, and strategic geographic understanding of the Maratha Empire (17th–19th century CE).
Why are they special?
They are not just individual forts. They are part of a military system – a cohesive, interconnected network that shows:
- Defense Planning across varied terrains: hills, coast, rivers.
- Architectural Innovation: Use of terrain rather than grand ornamentation.
- Geopolitical Control: These forts helped Marathas resist Mughal, Portuguese, and later British powers.
These forts are like living military textbooks, showing how an indigenous Indian empire used regional knowledge and indigenous engineering to build a defensive chain without relying on European models.
Strategic Geographic Understanding
The Marathas built these forts after studying geography deeply:
| Type of Fort | Purpose | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Hill Forts | Surveillance, defense, seat of power | Rajgad, Raigad, Pratapgad |
| Coastal Forts | Naval control, sea trade defense | Sindhudurg, Suvarnadurg, Vijaydurg |
| Island/Marine Forts | Early naval command posts | Khanderi Fort |
| Frontier Forts | To check enemy advance | Salher (northern border of Maratha territory) |
| Interior Control | Protecting movement corridors and capitals | Shivneri, Lohgad, Panhala |
This showcases the Maratha military genius: they used natural geography as part of defense, making their forts hard to siege.
Architectural Ingenuity
Unlike Mughal or Rajput forts, which were grand and decorative, Maratha forts had:
- Minimalist but robust design
- Locally sourced stone and lime
- Camouflaged architecture: they blended with the terrain.
- Advanced water management systems for sustainability during long sieges.
Key Point: The architecture was function-first – not to impress, but to withstand attacks, storms, and isolation.
Examples of Strategic Design
- Raigad Fort: Shivaji's capital; nearly inaccessible except by a single narrow path.
- Pratapgad Fort: Location of the famous 1659 battle with Afzal Khan, showcasing terrain-based tactical advantage.
- Vijaydurg: Called the "Gibraltar of the East" because it was almost unbreachable.
- Sindhudurg: Built by Shivaji using lime and lead — advanced tech for that time.
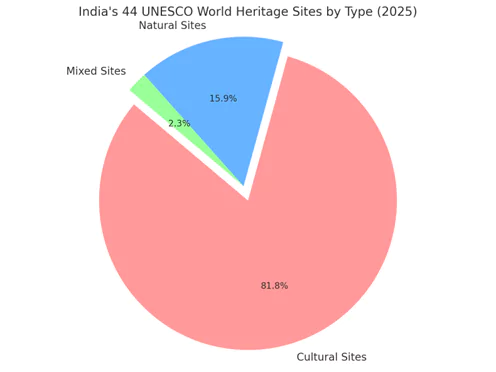
Total Sites in India: 44
These 44 sites are officially recognized by UNESCO for their Outstanding Universal Value (OUV) under the World Heritage Convention.
| Type of Site | Number | Percentage | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cultural | 36 | ~81.8% | Taj Mahal, Hampi, Jaipur, Maratha Forts |
| Natural | 7 | ~15.9% | Western Ghats, Sundarbans, Kaziranga |
| Mixed | 1 | ~2.3% | Khangchendzonga National Park |
India’s heritage recognition is culturally dominant, which reflects its ancient civilization, architectural diversity, and historical depth.
India’s Global and Regional Ranking (2025)
| Rank | Country | Number of Sites |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Italy | 59+ |
| 2 | China | 57+ |
| 3 | Germany | 52+ |
| 4 | France | 50+ |
| 5 | Spain | 49+ |
| 6 | India | 44 |
India is ranked 6th globally, surpassing many major Western nations in total count, and is 2nd in the Asia-Pacific region, only behind China.

Recent Key Additions (2023–2025):
| Year | Site Added | Type | Region | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | Moidams (Assam) | Cultural | Northeast India | Burial mounds of the Ahom dynasty |
| 2025 | Maratha Military Landscapes | Cultural | Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu | Military ingenuity of the Maratha Empire |
Why Moidams Matter:
- This was the first ever UNESCO cultural site from Northeast India—a historic milestone for regional representation.
Other global sites newly inscribed (2025):
- Cambodian Memorial Sites
- Forest Research Institute Malaysia Forest Park, Selangor
- Prehistoric Sites of Khorramabad Valley, Iran
Prelims Questions:
- Which of the following statements best describes the significance of the
Maratha Military Landscapes recently inscribed in the UNESCO World Heritage
List?
- They are grand palatial structures built by the Marathas to display imperial wealth.
- They are a network of forts built by the Marathas for trade and religious pilgrimages.
- They represent an indigenous and adaptive military architecture spread across diverse terrains.
- They are a set of forts constructed by the British to counter Maratha expansion.
- Which of the following correctly explains the architectural features of
Maratha Military Forts?
- Use of Persian domes and Indo-Islamic arches prominently
- Integration with terrain, minimal ornamentation, and strategic positioning
- Massive stone-cut pillars and rock-cut caves as main defensive elements
- Circular bastions and glazed tiles influenced by Portuguese architecture
- With reference to UNESCO World Heritage Sites in India, consider the
following statements:
- Maratha Military Landscapes are the first cultural World Heritage Site from the state of Maharashtra.
- India ranks among the top 10 countries globally in terms of total number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
- Khangchendzonga National Park is the only Mixed Heritage Site in India as of 2025.
- 1 and 2 only
- 2 and 3 only
- 1 and 3 only
- 1, 2 and 3
- Statement 1 is incorrect – Maharashtra already had Ajanta, Ellora, Elephanta, etc.
- Statement 2 is correct – India ranks 6th globally.
- Statement 3 is correct – Khangchendzonga is India's only Mixed Heritage Site.
Answer:C
Explanation: The forts showcase the Maratha Empire’s military innovation using regional topography for strategic defense.
Answer:B
Explanation: Maratha forts used the terrain as a natural defense, avoided grand ornamentation, and were constructed for military function.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
Answer:B
Explanation:
Mains Question:
- How do the World Heritage site’s recognitions contribute to India's soft power and cultural preservation efforts? 150 Words 10 Marks















