2024: The Hottest Year on Record
1. Overview
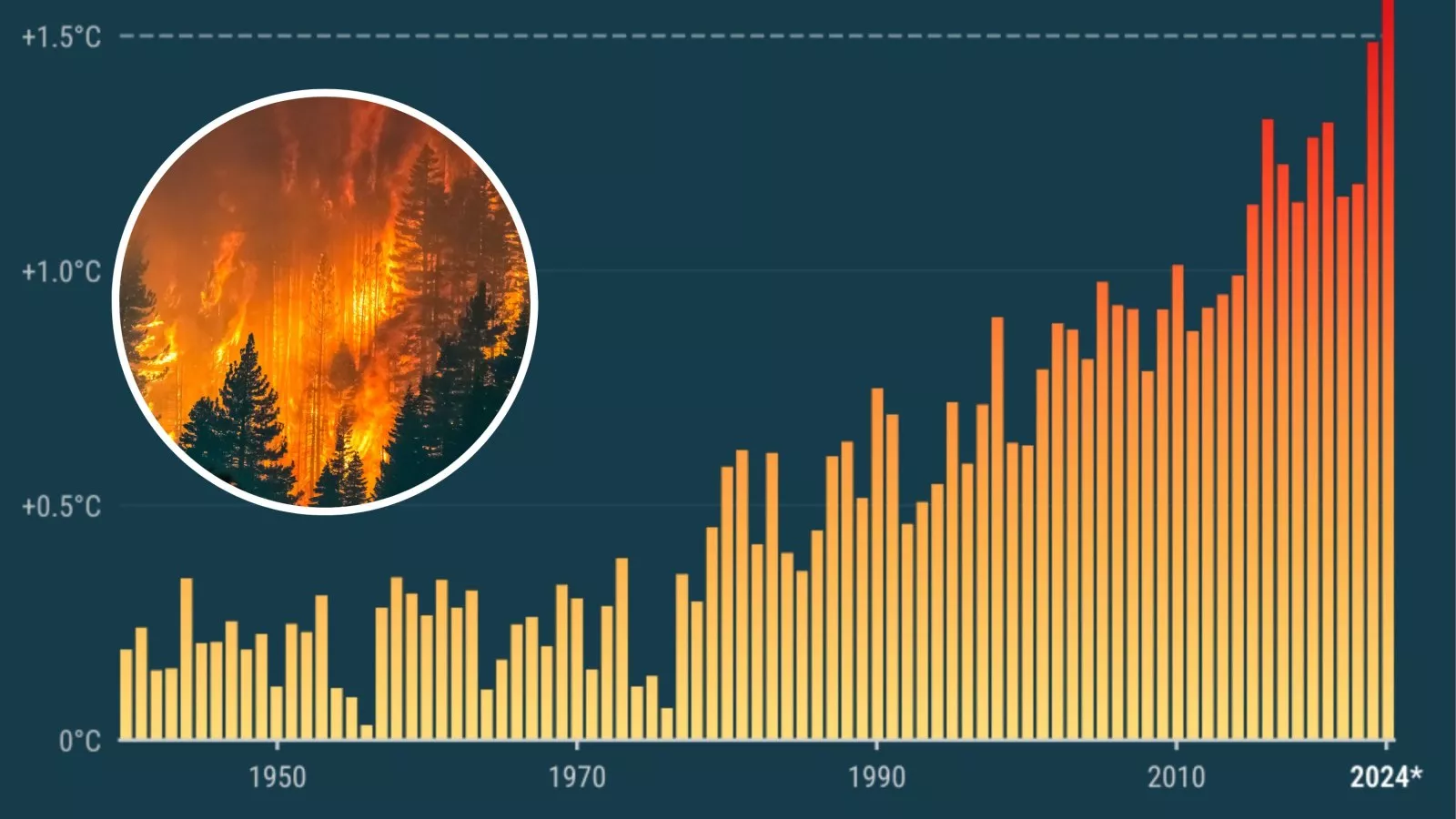
The year 2024 has surpassed 2023 as the hottest year on record globally. According to NASA and the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S), it is the first calendar year where the average global temperature exceeded 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels.
Key Findings:
- Global Average Temperature (2024):10°C, which is 1.60°C above pre-industrial levels and 0.12°C higher than 2023.
- Carbon Emissions: CO₂ levels reached 422 ppm and methane hit 1897 ppb, marking new record highs.
Key Temperature Records in 2024
- Hottest Year on Record:2024 surpassed 2023, marking a continued trend of increasing global temperatures.
- Hottest Day Recorded:July 22, 2024, with an Earth-wide average temperature of 16°C.
- Extreme Heat Stress: About 44% of the globe experienced strong to extreme heat stress, marking a 5% increase from previous years.
- Sea Surface Temperatures:
- Annual ocean surface temperature:87°C (0.51°C higher than the 1991-2020 average).
- Record marine heatwaves impacted ocean ecosystems and weather systems.
- Regional Heat Records:
- Europe's warmest year:67°C (1.47°C above the 1991-2020 average).
- Arctic warming:34°C above the 1991-2020 average, the fourth highest on record.
Factors Driving the Record-Breaking Temperatures in 2024
The unprecedented warming of 2024 was caused by a combination of anthropogenic (human-caused) factors and natural climate variability. While natural phenomena like El Niño played a role, scientists overwhelmingly agree that the dominant driver was greenhouse gas emissions and long-term climate change.
Below, we explore five major factors that contributed to 2024 becoming the hottest year on record:
Greenhouse Gas Emissions & the Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
-
The Role of Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) & Methane (CH₄)
- Carbon dioxide (CO₂) levels reached a record high of 422 ppm (parts per million) in 2024—an increase of 9 ppm from 2023.
- Methane (CH₄) levels hit 1897 ppb (parts per billion), an increase of 3 ppb over 2023.
- These gases trap outgoing infrared radiation, preventing heat from escaping into space.
- Effectively, more heat is retained in the atmosphere, increasing global temperatures.
-
The Long-Term Trend of Rising Emissions
- CO₂ levels have risen 50% since pre-industrial times (278 ppm in the 18th century to 422 ppm in 2024).
- This long-term accumulation of greenhouse gases (GHGs) is the primary reason for sustained global warming.
Key Impact:
- The more CO₂ and CH₄ in the atmosphere, the stronger the greenhouse effect, which means even in a year with a natural cooling effect, temperatures would remain high.
- The Earth is now heating up 10 times faster than during any previous natural warming period in history.
El Niño & Its Contribution to 2024's Extreme Heat
-
What is El Niño?
- El Niño is a natural climate pattern in the Pacific Ocean, which warms sea surface temperatures and disrupts weather patterns.
- The 2023-24 El Niño was exceptionally strong, pushing global temperatures above 1.5°C for extended periods.
- How El Niño Amplified Global Heat in 2024
- Warmer ocean waters release more heat into the atmosphere, raising global air temperatures.
- El Niño weakens trade winds, reducing the upwelling of cool, deep ocean waters, leading to a warmer climate overall.
- Increased evaporation leads to more humidity, intensifying heatwaves, storms, and extreme rainfall.
Key Impact:
- El Niño contributed an additional 1°C to 0.2°C warming, but the majority of the warming was due to long-term human-induced climate change.
- Even after El Niño weakened in late 2024, temperatures remained unusually high, proving that climate change is the dominant factor.
Decline in Aerosol Pollution & Reduced Solar Reflection
-
Aerosols & Their Cooling Effect
- Aerosols (tiny particles in the atmosphere) reflect sunlight back into space, providing a temporary cooling effect.
- Sulfate aerosols (produced by industrial pollution) previously helped offset some of the greenhouse effect.
-
Why Did Aerosol Pollution Decline in 2024?
- Stricter air pollution controls worldwide (e.g., reduction in sulfur emissions from shipping and coal plants).
- Cleaner energy sources replacing coal, reducing sulfate emissions.
-
How This Contributed to Warming
- With fewer sulfate aerosols reflecting sunlight, more heat was absorbed by the Earth.
- This effect is minor compared to GHG-induced warming, but it adds to the overall temperature rise.
Key Impact:
- Less aerosol pollution means the full force of CO₂-driven warming is being felt.
- While this improves air quality, it removes a temporary cooling effect that had slightly dampened global warming in previous decades.
Ocean Warming & Record-Breaking Sea Surface Temperatures (SSTs)
- Record Ocean Temperatures in 2024
- The global ocean surface temperature reached an all-time high of 20.87°C.
- This is 51°C above the 1991-2020 average.
- The North Atlantic, Indian Ocean, and Western Pacific recorded unprecedented marine heatwaves.
- How Warmer Oceans Contribute to Global Warming
- Oceans absorb 90% of excess heat from greenhouse gases.
- Warmer oceans release more heat into the atmosphere, amplifying air temperatures.
- Extreme marine heatwaves intensified hurricanes, typhoons, and heavy rainfall events.
Key Impact:
- The higher ocean temperatures in 2024 fueled stronger storms, more extreme weather, and higher humidity, leading to prolonged heatwaves.
- This effect will persist for years, even if emissions are cut today, because oceans store and slowly release heat.
Stratospheric Water Vapor & the Role of the Tonga Volcanic Eruption
- The 2022 Tonga Volcanic Eruption's Impact on Climate
- The Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha’apai eruption (January 2022) injected unprecedented amounts of water vapor into the stratosphere.
- Unlike typical volcanic eruptions that cool the planet (due to sulfate aerosols), this eruption had a warming effect.
- How Water Vapor Contributed to 2024’s Warming
- Water vapor is a powerful greenhouse gas, trapping more heat than CO₂ in the short term.
- The eruption increased stratospheric water vapor by 10%, intensifying the greenhouse effect.
Key Impact:
- This additional water vapor warming could have added 0.05°C to 0.1°C to global temperatures in 2024.
- This is a secondary factor, but it shows how natural events can amplify human-caused climate change.
Regional Impacts of 2024 Climate Extremes: A Highly Detailed Analysis
The year 2024 was marked by unprecedented climate extremes, with heatwaves, wildfires, hurricanes, droughts, and floods affecting nearly every continent. While global temperature rose by 1.60°C above pre-industrial levels, regional variations in geography, atmospheric patterns, and ocean currents dictated the severity and nature of these climate impacts.
In this section, we will explore how different regions across the world were affected by the record-breaking global temperatures of 2024, analyzing specific climate disasters, their consequences, and long-term implications.
North America: Record-Breaking Heat, Wildfires & Hurricanes
- United States: Extreme Heatwaves & Climate Disasters
- 2024 was the hottest year on record for the U.S., with extreme heat events impacting nearly all states.
- Phoenix, Arizona: Recorded 113 consecutive days above 100°F (37.8°C), breaking all previous records.
- Texas & Florida:
- Heat index exceeded 50°C (122°F) on multiple days.
- Power grid failures due to high air conditioning demand led to widespread blackouts.
- Heat-Related Deaths: The U.S. reported over 2,300 heatstroke deaths, the highest in modern history.
- Wildfires in Canada & the U.S.
- Canada: Witnessed its worst wildfire season ever, burning over 5 million hectares of forests.
- California & Oregon:
- Over 800,000 acres destroyed by wildfires.
- Smoke from these wildfires created hazardous air quality, affecting New York, Chicago, and Toronto.
- Strongest Hurricanes on Record
- Hurricane Beryl (June 2024)
- Earliest Category 5 hurricane ever recorded in the Atlantic.
- Winds reached 185 mph, causing catastrophic flooding in Texas, Louisiana, and the Caribbean.
- Hurricane Milton (September 2024)
- Intensified by 95 mph within 24 hours, a sign of rapid intensification fueled by warmer ocean waters.
- Devastated Florida, Georgia, and the Carolinas, causing $20 billion in damages.
- Hurricane Beryl (June 2024)
Europe: Hottest Year in History & Deadly Heatwaves
- Record Heat in Southern & Western Europe
- Europe recorded an average temperature of 10.67°C, which was 47°C above the 1991-2020 average.
- France, Spain, and Italy saw temperature spikes of over 45°C (113°F) for multiple consecutive days.
- Germany & UK:
- Heatwaves exceeded 40°C (104°F), causing infrastructure failures and railway disruptions.
- Water shortages in Germany led to rationing in some cities.
- Extreme Droughts & Water Crisis
- Spain & Portugal:
- The Iberian Peninsula faced its worst drought in 500 years.
- Agriculture collapse: Olive, wheat, and wine production dropped by 30%, impacting global food markets.
- Italy’s Po River Drought:
- The Po River fell to historic lows, threatening irrigation for millions of farmers.
- Spain & Portugal:
- Floods & Storms in Northern & Central
Europe
- Storm Helga (October 2024):
- Winds of 120 mph caused extensive flooding in Germany, Netherlands, and Belgium.
- United Kingdom:
- London and Manchester saw record-breaking rainfall, leading to subway shutdowns and power outages.
- Storm Helga (October 2024):
Asia: Deadly Heatwaves, Monsoon Shifts & Glacier Melting
- India & South Asia: Worst Heatwaves in Recorded History
- Delhi recorded 52.1°C (126°F), the highest temperature ever in the capital city.
- States of Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Bihar saw over 2,000 heatstroke deaths.
- Agricultural Impact:
- Wheat production fell by 15%, threatening food security.
- Rice yields dropped, causing export bans.
- Monsoon Disruptions & Flooding
- Delayed monsoon onset led to extreme droughts in South India, while North India saw excessive rainfall.
- Mumbai & Chennai:
- Unprecedented urban flooding, submerging roads and train stations.
- Pakistan & Bangladesh:
- Heavy rainfall caused landslides in hilly regions, displacing over 500,000 people.
- Himalayan Glacier Melting & Water Security Threats
- The Himalayan glaciers shrank by 65% faster than expected, threatening water supply to India, Nepal, and China.
- Scientists warn that Ganges and Indus river basins could face severe water shortages by 2035.
Africa: Droughts, Famine & Disease Outbreaks
- East Africa: Prolonged Droughts & Food Crisis
- Kenya, Ethiopia, and Somalia experienced their worst drought in 60 years.
- Agricultural Collapse:
- Maize and sorghum production dropped by 50%.
- Millions faced acute food shortages and famine conditions.
- Disease Outbreaks & Rising Malaria Cases
- Malaria & Dengue Fever Expanded as warmer temperatures created new mosquito-breeding grounds.
- Sudan & Chad:
- Cholera outbreaks surged due to contaminated water sources.
South America: Heatwaves, Amazon Fires & Climate Disasters
- Amazon Rainforest Fires
- Brazil recorded the highest number of wildfires in the Amazon since 2019.
- The Amazon Basin lost over 3.2 million hectares of forest, worsening global carbon emissions.
- Heatwaves & Water Shortages in Argentina & Chile
- Buenos Aires recorded 3°C (117°F), causing massive power blackouts.
- Chile’s water reservoirs fell below 30%, forcing emergency conservation efforts.
Oceans & Polar Regions: Melting Ice, Sea Level Rise & Marine Heatwaves
- Arctic & Antarctic Melting Accelerates
- Arctic temperatures were 1.34°C above normal, leading to record-low summer ice cover.
- Antarctica’s Thwaites Glacier ("Doomsday Glacier") showed rapid melting, increasing concerns of sea level rise.
- Global Marine Heatwaves & Coral Bleaching
- Great Barrier Reef:
- Over 50% of coral reefs bleached, threatening marine biodiversity.
- Great Barrier Reef:
- North Atlantic & Indian Oceans:
- Record-breaking ocean temperatures fueled stronger hurricanes and typhoons.
Economic & Societal Impacts of 2024 Climate Extremes
The year 2024, the hottest year on record, brought severe economic and societal disruptions across the globe. From agriculture and food security crises to power grid failures, infrastructure damage, and increased public health burdens, the economic cost of climate change soared to trillions of dollars worldwide.
This section provides a highly detailed breakdown of how different economic sectors and societal systems were affected by heatwaves, wildfires, droughts, floods, hurricanes, and rising sea levels.
Global Economic Costs of Climate Disasters in 2024
- Direct Economic Losses from Climate Disasters
- The total economic loss from climate-related disasters in 2024 exceeded $2.5 trillion globally, making it the costliest year for climate-related damages in recorded history.
- The United States alone suffered over $420 billion in damages, while Europe, China, and India saw combined losses of over $1 trillion.
- Insurance claims skyrocketed, with global reinsurance firms warning of higher premiums and potential industry collapse in high-risk areas.
- Sectoral Breakdown of Economic Losses
Sector Estimated Loss in 2024 Agriculture & Food Security $500 billion Infrastructure & Urban Damage $700 billion Energy & Power Grid Failures $350 billion Health Sector & Emergency Response $250 billion Displacement & Humanitarian Aid $180 billion Insurance Payouts $500 billion Total Estimated Loss $2.5+ trillion
Agriculture & Food Security: Crop Failures & Rising Prices
- Widespread Crop Failures
- Heatwaves, droughts, and floods destroyed millions of hectares of crops worldwide.
- India:
- Wheat yields dropped by 15% due to extreme heat, forcing the government to ban wheat exports.
- Rice production declined, leading to a 10% price surge in global markets.
- United States:
- Corn and soybean yields fell by 20% in the Midwest due to record heat and drought.
- Europe:
- The olive oil sector in Spain collapsed, with 80% yield reductions due to prolonged drought.
- Africa:
- Famine conditions worsened in Kenya, Ethiopia, and Sudan, affecting millions.
- Food Prices & Global Inflation
- Food prices increased by an average of 12% worldwide in 2024 due to crop losses.
- Staple foods (wheat, rice, corn, and soybeans) saw price spikes of 20-40% in global markets.
- Developing nations faced severe food insecurity, with millions pushed into hunger.
Energy Crisis: Power Grid Failures & Increased Demand
- Record Power Demand & Blackouts
- Extreme heat drove up electricity demand, overwhelming power grids.
- Texas, California, and parts of India faced weeks-long rolling blackouts.
- European countries like Spain, Germany, and Italy saw electricity rationing, particularly for industrial use.
- Strain on Renewable Energy
- Hydropower production fell by 15-25% in drought-hit regions like Brazil, the U.S., and China.
- Solar and wind farms struggled as heat reduced efficiency and strong storms damaged infrastructure.
- Fossil Fuel Dependence Increased
- Due to power shortages, many countries ramped up coal and oil production, temporarily increasing carbon emissions despite climate pledges.
Infrastructure Damage & Urban Heat Island Effect
- Transportation & Roadway Failures
- Asphalt roads melted in India, the Middle East, and parts of the U.S., causing massive traffic disruptions.
- Railway tracks warped due to extreme heat, delaying trains across Europe and North America.
- Flooding submerged major highways in Japan, Germany, and China, leading to billions in repair costs.
- Urban Heat Islands & Housing Crisis
- Cities experienced record-breaking nighttime temperatures, worsening the urban heat island effect.
- Low-income communities suffered the most, as many lacked air conditioning or access to cooling centers.
- Increased housing damage in coastal areas led to a spike in climate-related migration.
Health & Public Safety: Heat-Related Deaths & Disease Outbreaks
- Heat-Related Mortalit
- Over 50,000 excess deaths globally were attributed to extreme heat.
- India & Pakistan:Thousands of heatstroke deaths, particularly among laborers and the elderly.
- Europe:Heatwaves caused over 15,000 premature deaths, surpassing the 2003 European heatwave death toll.
- Spread of Infectious Diseases
- Warmer temperatures expanded mosquito breeding grounds, leading to a global spike in malaria and dengue cases.
- Africa & South America saw cholera outbreaks, worsened by flood-related water contamination.
Human Displacement & Climate Refugees
- Over 50 million people were displaced by climate disasters in 2024.
- South Asia:
- Extreme flooding in Bangladesh displaced 10 million people.
- Africa:
- Drought and desertification forced mass migrations from Somalia and Ethiopia.
- United States:
- Hurricanes and wildfires caused thousands to flee coastal regions and the West Coast.
- The cost of housing climate refugees exceeded $180 billion
- Cities struggled with increased pressure on housing, food supply, and healthcare systems.
Financial & Insurance Industry Impact
- Collapse of Insurance Markets in High-Risk Areas
- Global insurance claims exceeded $500 billion, making 2024 the costliest year for insurance firms.
- Many insurance companies stopped covering homes in flood-prone and fire-prone areas like California, Florida, and Australia.
- Governments had to step in with climate risk funds, adding financial strain.
- Stock Market & Economic Slowdown
- Climate disasters disrupted global supply chains, causing stock market instability.
- Food and energy companies saw massive price fluctuations, contributing to inflation spikes worldwide.
Way Forward & Conclusion
Urgent Action Needed to Combat Climate Crisis
The record-breaking heat and climate disasters of 2024 are a wake-up call. The world is at a tipping point, with $2.5+ trillion in economic losses, millions displaced, and ecosystems collapsing. If immediate action is not taken, climate extremes will become more frequent and devastating.
Key Solutions for a Sustainable Future
- Rapid Emission Cuts: Nations must accelerate carbon reduction by shifting to renewable energy and enforcing strict emission policies.
- Climate Resilient Infrastructure: Cities must adopt heat-resistant buildings, expand cooling solutions, and invest in flood protection.
- Food & Water Security: Sustainable agriculture, drought-resistant crops, and efficient irrigation are crucial.
- Energy Transition:Phasing out fossil fuels while improving energy storage & grid resilience will prevent future power crises.
- Climate Finance & Policy Reforms: Wealthier nations must fund climate adaptation programs in vulnerable regions to prevent mass displacement & economic collapse.
- Public Awareness & Lifestyle Change: Individuals must embrace sustainable habits, including reduced consumption, energy conservation, and climate-conscious choices.
A Defining Moment for Humanity
The future is in our hands. Swift and decisive action today can prevent irreversible climate catastrophe. Every degree of warming we avoid protects millions of lives, ecosystems, and economies. The time to act is NOW—before it's too late.
Practice questions for mains
- "The year 2024 has marked a significant turning point in global climate history, with unprecedented heatwaves, economic disruptions, and environmental crises. Analyze the primary causes of record-breaking temperatures in 2024 and discuss the immediate and long-term policy measures required to mitigate the climate crisis."(250 words, 15 marks)
- "With 2024 becoming the hottest year on record, the global economy and human societies have faced severe disruptions. Critically examine the economic and societal impacts of extreme climate events in 2024, and suggest adaptive strategies to enhance resilience in developing and developed nations."(250 words, 15 marks)












